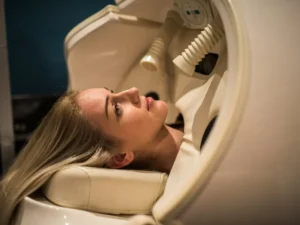
Oxygen Therapy Is Safe and Non-Invasive – The Truth
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy is considered a safe and non-invasive treatment method. It involves inhaling pure oxygen at increased pressure in a hyperbaric chamber designed specifically for this purpose. Thanks to this, oxygen reaches all body cells faster and in larger quantities (including those where oxygen access is difficult under normal conditions, e.g. cartilage, joints, eyeballs), which contributes to the creation of new blood vessels, nerves and acceleration of regeneration processes. It is worth noting that hyperbaric oxygen therapy is safe when the patient has no contraindications to the use of this therapy and only when it is carried out by trained personnel or the person using it on themselves has been trained by a specialist in hyperbaria or normobaria.
Oxygen therapy causes side effects – a myth
Although hyperbaric oxygen therapy is considered a safe treatment method, there are several contraindications to its use, such as certain lung or heart diseases. However, if the therapy is properly selected for the patient and carried out by qualified personnel,
the risk of side effects is minimal . In rare cases, symptoms such as dizziness or fatigue may occur, which usually disappear after the session ends.
Oxygen therapy is only used to treat respiratory diseases – a myth
Although hyperbaric oxygen is often associated with the treatment of respiratory diseases, such as asthma, its application is much broader. This therapy can also be used in the treatment of burns , wounds that are difficult to heal, carbon monoxide poisoning or in the treatment of some bacterial infections. In addition, it is increasingly used as a supportive therapy in cleansing the body of toxins and heavy metals, reducing inflammation (including hidden ones), in the case of Lyme disease, in the field of neurology and oncology.
Oxygen Therapy Speeds Up Recovery After Exercise – The Truth
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy is increasingly used in sports as a method supporting the regeneration of the body after intense physical effort. Increased concentration of oxygen in the blood accelerates repair processes in the muscles, which shortens the time needed to return to full fitness, as well as increases the body’s efficiency. In addition, hyperbaric and normobaric oxygen therapy promotes the production and deposition of collagen in tissues, reduces inflammation, increases the amount of ATP in cells and shortens the problem of “muscle acidification”, commonly called “soreness”. Many people also use this therapy after injuries or surgeries to speed up the healing of wounds and reduce the risk of complications.